This article is a part of our Content Hub. For more in-depth resources, check out our content hub on Mobile App Testing Tutorial.
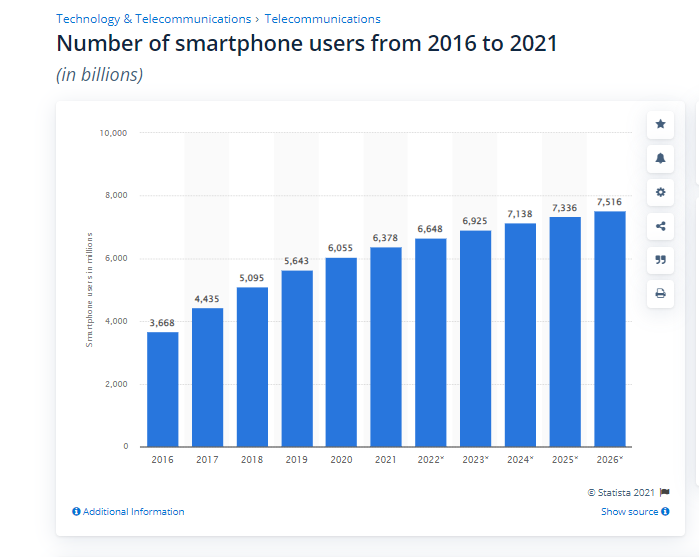
It’s no wonder that the mobile app industry is booming, with over 3.2 billion smartphone users globally. Since the COVID-19 pandemic, mobile app downloads increased by 23.3% worldwide in 2020. According to Gartner, smartphones were sold 10.2% more globally only in the second quarter of 2021, despite the COVID-19 pandemic.
This is enough evidence to show that mobile apps and mobile app testing are especially significant in recent times. By 2023, mobile applications are expected to generate more than $935 billion in revenue. Therefore it’s important to have the right mobile app testing strategy to smoke the competition.

Source
For an ultimate mobile app experience across different mobile devices and OS versions, it is crucial to perform end-to-end mobile app testing.
This article covers the basics of mobile app testing, types of mobile apps, and the frameworks and tools to develop and test them.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Mobile app testing plays a critical role in ensuring applications work efficiently on all mobile devices and their OS versions. 2020 noted 218 billion mobile app downloads, thus reinstating the importance of deploying well-planned applications to draw users’ attention. Mobile application testing typically refers to checking functional and non-functional components of an app. In addition, highly skilled experts test its consistency, usability, performance, and compatibility across various platforms and devices.
A mobile application goes through several rounds of testing before it is released for end users. Corporates with big budgets also often launch a beta version of their apps to detect and eliminate bugs in the prototype. Several mobile app testing tools aid technical teams in carrying on the intricate testing procedures.
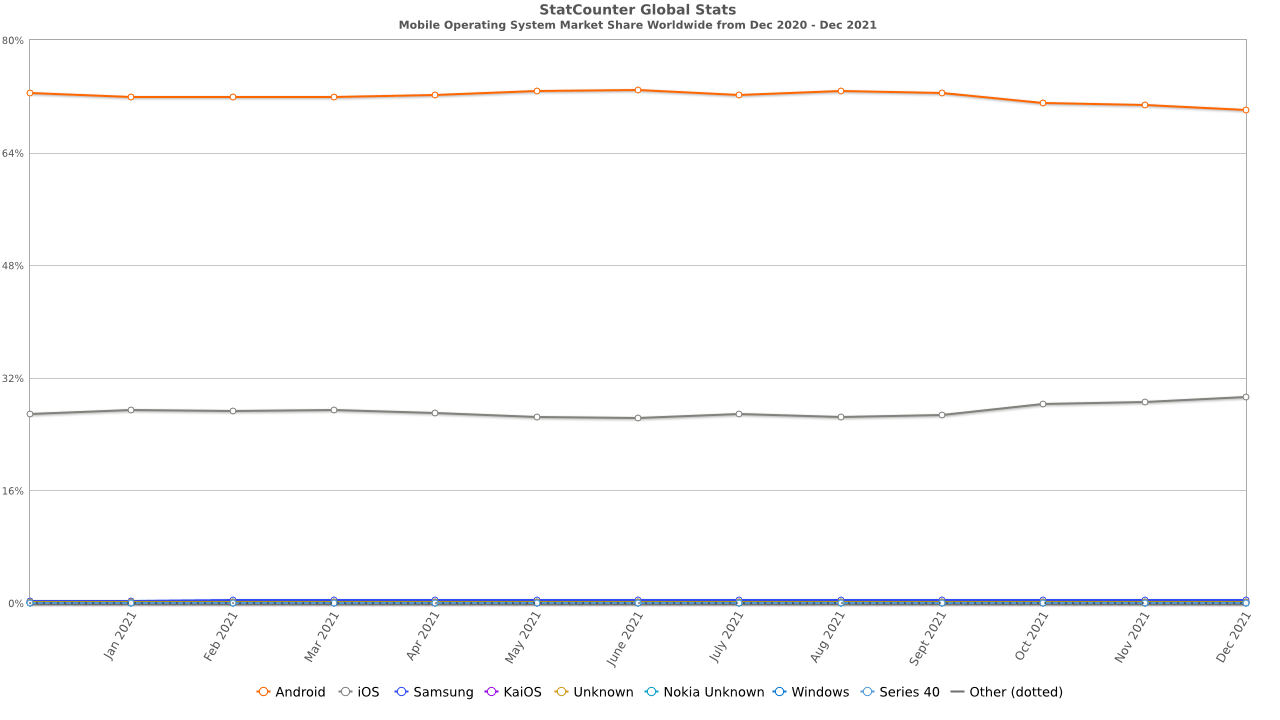
Developed by Google and launched in 2008, Android is currently the most popular mobile operating system globally. As of September 2021, 72.44% of global smartphones run on Android. Hence, most mobile phone users across the world use Android, which makes it all the more important to test applications built to work on this platform.
Source
The following tests are typically performed on Android apps to test real-world scenarios.
Apple is one of the leading tech companies globally, quadrupling its growth in the last decade. In 2021, Apple earned a revenue of $365.82 billion, a whopping increase from its 2020’s $74.52 billion. In addition, the company has its own operating system, iOS, that powers all its mobile phones. From its popularity, it is not hard to guess how vast its app market must be to align with the growing needs of its users.
Since iOS has a limitation- it is available only on Apple devices, it is much easier to test iOS apps due to reduced device complexities.
Here are a few advantages of testing iOS apps:
Here is a quick video tutorial on the Android and iOS app testing on real devices.
In a world where different types of apps are being developed for multiple uses, understanding the app complexities in detail has become a critical requirement for success in the app world. Although there are many different types of apps on the market, we will cover Native, Hybrid, and Web Apps.
Native apps are applications built for one specific operating system or platform. Such apps are faster and deliver superior performance due to the ease of interaction between their interface and hardware and software. In addition, since native apps are developed to work on one platform, they can directly use the features made available by the architecture of the gadget.
While creating native apps for iOS or Android, developers use the most popular coding languages for the platform. Native apps for Apple’s iOS are built using Swift or Objective-C, while those for Google’s Android are developed using Java. Native applications like WhatsApp are built separately for all the available operating systems to ensure top-notch performance for all devices.
Automate your mobile app testing on Apple or Android for free.
WhatsApp has maintained its position as the most popular messaging app, with 2 billion active users every month across the globe. Since its inception in 2009, the application has become a staple for personal and professional conversations without the constraints of time zones and national boundaries.
WhatsApp is a native app developed by Jan Koum and Brian Acton in 2009. In 2014, Meta acquired it (previously known as Facebook). Since then, WhatsApp has gone through many changes, each of which has made it more robust. WhatsApp is known for its efficient performance, high-quality video and voice calls, and easy media sharing options. All of its advantages are a direct result of its native nature that allowed the developers to explore the full potential of the respective operating systems.
Another popular native app in the global market is Spotify. It is the multibillion-dollar music streaming application launched in 2006. The second quarter of 2021 noted 172 million subscribers to Spotify Premium. During the same time, in 2020, they had 144 million paid members.
Spotify uses modern technologies like Conventional Neural Network or CNN to evaluate music. Its algorithms are highly efficient in detecting a song’s volume, key, and tempo utilizing only the audio waveform. Spotify is further supported by the Google Cloud infrastructure that, in conjunction with its native features, helps it deliver high performance.
Web apps are web components that a user can use to achieve an outcome. Web applications are typically stored on remote servers and accessed through browsers on the user’s computer- desktop, cell phones, and tablets alike. The wide appeal of web apps stems from their high usability factor. Anyone can launch a website within a short time, with minimum resources, and still draw substantial global attention.
A good web application works fast and efficiently displays everything correctly. For example, 47% of viewers expect a web page to load in two seconds or less, thereby making efficiency a top priority for developers and mobile app testing teams.
Google Docs is a real-time word processing web app that is free to use. It allows multiple users to write and edit as collaborators and automatically saves the document to Google Drive. The web application was built using Java and JavaScript, giving it a clean, easy-to-use interface.
One of the most popular OTT platforms globally, Netflix serves 214 million subscribers in 190 countries worldwide. It is a web application supported by languages like Python, Kotlin, Java, and JavaScript. Netflix is known for delivering superb performance and maintaining a high customer satisfaction rate.
Hybrid apps are developed using a combination of native and web app features. They have the shell of a native application over the underlying tech stack of their web-based counterparts. In addition, hybrid apps are typically built over a single code base for all platforms, facilitating high code reusability.
Hybrid apps are an attractive solution to a wider market because of their cost-effective, quicker development process. These apps are worldwidemanylightweight and have a user interface comparable to that of a native app. In addition, hybrid apps can be built using a web app technology stack that typically consists of HTML5, CSS, and JavaScript.
Gmail is the most widely used emailing platform and has 1.8 billion users around the globe. Launched by Google in 2004, Gmail has many variations- including a web app version. It has an elaborate user interface initially designed by Kevin Fox, who wanted the platform to feel like a one-page application.
One of Gmail’s advanced features is its spam filter and is driven by the community of users. The spam filter is an intelligent algorithm that learns from when a user marks an email as spam and identifies similar messages in other inboxes around the world. In 2020, 306.4 billion emails were exchanged globally every day.
The current annual revenue of Twitter is $3.72 billion. It is safe to say the social media app has created quite a stir with its presence alone. The platform is a stellar example of a hybrid app and highlights how powerful a well-made application of this nature can be. As of Q2 of 2021, Twitter had 206 million active users every day. This is enough to demonstrate the kind of traffic the app has to handle regularly without crashing down.
Twitter delivers excellent performance due to its hybrid nature. Hybrid applications do not depend on the network connection to completely load the app onto the device. This feature instantly introduces hybrid apps to a vast arena of users who lack good network connectivity. Moreover, since the loading does not depend on the Internet, it becomes superbly easy for the interface to manage traffic.
With so many apps released each year, it is critical to understand the difference between web, hybrid, and native apps.
A mobile app framework is a software development package that integrates tools and software, compilers, debugging tools, and programming interfaces. The developer then creates the source code for the application and the framework and uses various elements to develop the application for the different mobile devices.
Some mobile app development frameworks for both Android and iOS are listed below.

Developed by Facebook, React Native is one of the most widely used mobile app development frameworks. In addition, it is open-source and supports the creation of both iOS and Android apps, thus making it a first preference among the developer community.
Flutter is a popular software development kit or SDK used globally for cross-platform mobile application development. Hence, it provides developers with the ability to build Android, iOS, and Windows apps using a single Codebase. Although it started simply as a startup, Google acquired it before planting its roots in the software community.
Xamarin, a Microsoft product, uses C# and .NET to build Android, iOS, Apple Watch, and Wear applications. Xamarin is famous for being a time and cost-effective solution for cross-platform mobile app development.
Below are the popular frameworks for Android automation testing and iOS automation testing of mobile applications.
Appium is another mobile app automation testing tool to automate web, native, and hybrid mobile app testing on all mobile and desktop platforms. Apps do not need recompilation or modification and do not need to adhere to any specific languages for Appium to automate their tests. Also open-source like Selenium, Appium proves to be a powerful tool for developers to play around with. Run your free mobile tests on Appium grid.
Looking to automate mobile apps on real devices, check out our video below –
A software development company, Ranorex GmbH, provides this framework. It is a GUI test automation platform that facilitates testing all kinds of mobile applications. Ranorex Studio supports languages such as VB.NET and C#.
Categorized under the Apache project, Apache JMeter is used heavily as a load testing tool. In addition, it is utilized to measure and analyze various services, especially web applications for mobile. But JMeter can also be used as a unit testing tool and has its architecture based on plugins.
To know more about app testing frameworks, you can refer to our blog on the best mobile app testing frameworks for Android and iOS apps.
Mobile app testing helps identify flaws in mobile apps and refine them for the intended audience. Therefore, it is critical to consider the various key types of app testing to understand the multiple perspectives for evaluating an app’s potential performance.
Below are the listed key types of Mobile App Testing.
Functional testing of mobile applications checks whether the app is functioning correctly. This kind of test ensures the components are behaving as they should- they are responsive, true to their purpose, meet the required specifications, and the flow of the app is being maintained.
Example: Suppose an e-commerce app needs to be tested for functionality. Here, a product can be added to the cart to check the ‘Add to cart’ feature is working fine. The customer can then proceed to checkout to ensure that the payment features are working.
Usability testing brings the user’s experience to the forefront. It checks how user-friendly a mobile app is if it requires bug fixes, how intuitive its interface is, and how easy it is to navigate through the application. Usability testing provides a holistic report of a customer’s feedback while using the application.
Example: A mobile app usability testing example would be creating a survey of questions that an end-user is asked to answer after using an app for a while. This can provide great insight into what needs to be further modified.
Compatibility testing is a non-functional technique that checks if an application is ready to deliver great performance on multiple devices and operating systems, in specific network conditions, and with various hardware specifications.
Example: An app like Amazon Prime Video can be tested to check if it is running on all devices- mobiles, desktops, TVs, tablets, etc., of all specifications.
Performance and load testing ensure an application is not performing poorly under specific workloads. In addition, these tests provide the device resource consumption, like battery, time, and memory are not being expended to a great extent.
Load and performance testing also checks for network delays, the performance of servers, and the format in which data is being sent and received at the backend. Applications should also have an inherent backup and recovery system for an unprecedented data loss.
Example: A typical example of load and performance testing is running tests on an e-commerce app before a big sale day. Due to heavy traffic, there are high chances of the application crashing mid-way. Performance and load testing can stop that from happening.
Security is one of the deciding factors behind whether a person will download and use the app or not. Unless data privacy, authenticity, and integrity are ensured, users will never feel comfortable using an app, especially since most applications ask permission to access a user’s private information. Hence, security testing is imperative to ensure users’ data is safe and well protected.
Example: An SSL protocol is used by website or web app owners and developers to authenticate communication and data exchange between the client and the server.
Installation testing checks if the installation and uninstallation procedures of an application are smooth and without hassles. This kind of testing also ensures the updates to an app are without errors and undisturbed.
Example: While installation testing, network connectivity can be checked by changing the device connection from WiFi to 4G cellular data. Ideally, the installation should not be interrupted, and the procedure should continue irrespective of this alteration.
Localizing testing ensures an application is ready to be used in various local markets. From a change in currencies to a change in cultures, an app should ideally be able to handle all that, especially if it is targeting a wide demography of audiences around the globe.
Users expect their applications to run smoothly and represent them while solving their particular problems with unique solutions. Therefore, consumers tend to lose interest if an app is not aligned with these clauses.
Example: Running tests to ensure an e-commerce site in the US, the UK, and India has a currency changing feature for the appropriate location.
Device testing is an essential part of the mobile app testing process. Many applications’ functionalities depend highly on a mobile’s internal hardware specifications and operating system. Device testing ensures an app is ready to run on a spectrum of devices with any combination of specifications.
For example, since building physical infrastructure to support this is quite cumbersome, the LambdaTest Mobile app testing platform can come in handy here. It provides a wide range of 3000+ devices and OS combinations on the cloud that testing teams can exploit to ensure their app is running everywhere and under all conditions.
Mobile testing can be performed using one of two methods:
Testing mobile apps manually rely solely on a human to test an application from scratch until the end. This means the quality assurance testers cannot use automation tools, scripts, or other resources to carry on these tests. To begin with, this sounds ghastly, especially when one imagines the number of tests that must be run to ensure one application will perform well in the real world. Hence, one might be tempted to do away with manual testing completely.
However, discarding manual tests is unwarranted as the end-users are still humans, and automation, no matter how beneficial, time, and cost-effective, might not be prepared to guarantee the way an app feels to a real, breathing consumer of flesh and blood. Hence, manual testing is needed and still performed reasonably, just as a final nudge of reassurance for the testing team.
Automated mobile testing eg. android automation testing is the need of the hour when it comes to running multiple application tests. Here, testing teams use mobile app testing tools for automation and testing clouds to test the functionality and viability of an app in multiple conditions. Automated tests are typically used where a number of tests need to be run simultaneously. However, developers and testers still have to partially rely on human supervision in complex cases.
Automated mobile app testing is fast, efficient, and affordable. It does not require setting up a huge infrastructure of physical devices as would have been necessary for manual mobile app testing. In addition, almost all tests can be performed using the cloud, which leading companies like LambdaTest provide.
LambdaTest enables you to test mobile apps on real devices, simulators, and Android emulators online. As a result, you run the tests and detect bugs across multiple Android and iOS devices early in the development cycle. This enables you to replace your expensive in-house device labs with a mobile testing cloud for all manual and automated app testing requirements. Have a look at this seminar brief that talks about end to end mobile testing. Before you kick start Mobile app testing, refer to this ultimate mobile app testing checklist for carrying out effective mobile device cloud testing.
Test your Locally Hosted apps Using the LambdaTest Tunnel, you can ensure the sanctity of your locally hosted or privately hosted apps by running test on Vivo emulators. No complicated set up, Underpass will do it for you. Start your free test now!

Note
Kick start mobile app testing journey for free. Try LambdaTest Today!
You can also test apps on LambdaTest real device cloud to test real-world scenarios of your app. The real device cloud for Mobile app testing allows users to access real devices and test their apps on a variety of real Android and iOS devices. Using real device cloud testing, you can test your native apps for functionality, compatibility, and reliability. For real devices you can configure your automation frameworks tests through our real device capabilities generator.
Here is a quick rundown of the features offered by LambdaTest Mobile App Testing Platform.
Mobile app testing is an important part of a mobile application’s life cycle. While Android apps seem to have the greatest hold in the global app market, Apple is much more classified and sophisticated while dealing with applications created for iOS. Mobile app development frameworks and tools help developers and testers build state-of-the-art applications for Android, iOS, and Windows operating systems before sending them to various app stores.
In this article, we explored the basics of mobile application testing to understand the topic as a whole and in parts with respect to testing applications for Android and iOS. We also discussed types of apps, mobile development frameworks and tools, and how LambdaTest – a cloud test execution platform caters to your Mobile testing needs.
You can test Mobile applications on various Android and iOS devices either using real devices or emulators and simulators. Testing on real devices allows users to test apps in real-world scenarios. While testing on emulators or simulators can be beneficial in the early stages of development, they are not reliable enough to ensure the efficacy of applications in real-world user environments.
Shown below are the types of Mobile testing:
Writer, AI/ML student, and enthusiast, an avid reader. Works with companies from across the globe has mentored more than 500 students in content writing and has a team of 10 talented writers who help her with her projects. Loves art and cats.
Writer, AI/ML student, and enthusiast, an avid reader. Works with companies from across the globe has mentored more than 500 students in content writing and has a team of 10 talented writers who help her with her projects. Loves art and cats.
Got Questions? Drop them on LambdaTest Community. Visit now

Signup for free